The healthcare industry relies heavily on skilled professionals to ensure smooth operations and high-quality services. Among them, healthcare support professionals and clinical medical assistants play pivotal roles. If you’re exploring a career in medical assisting or simply curious about how these roles differ, understanding the clinical medical assistant vs medical assistant comparison is essential. Moreover, with increasing concerns around Healthcare Data Breach incidents, the importance of trained and compliant medical staff has never been more critical.
This post will walk you through the key distinctions, job responsibilities, and core functions of a clinical medical assistant vs healthcare support professional, so you can better understand their unique contributions within a medical setting.
Introduction to Medical Assistants
Healthcare support specialists, including medical assistants, play a vital role in the healthcare industry, providing essential assistance to healthcare professionals in various medical settings. They are responsible for performing both administrative and clinical duties, making them an integral part of medical staff operations.
These professionals work closely with patients, taking medical histories, recording vital signs, and preparing them for medical assessments. They also handle administrative tasks such as scheduling appointments, maintaining medical records, and managing insurance forms.
Clinical Medical Assistant vs. Medical Assistant
The primary difference between a clinical medical assistant and a medical assistant lies in their roles and areas of focus within a healthcare setting. While both positions require similar educational backgrounds and certifications, their job responsibilities may vary significantly.
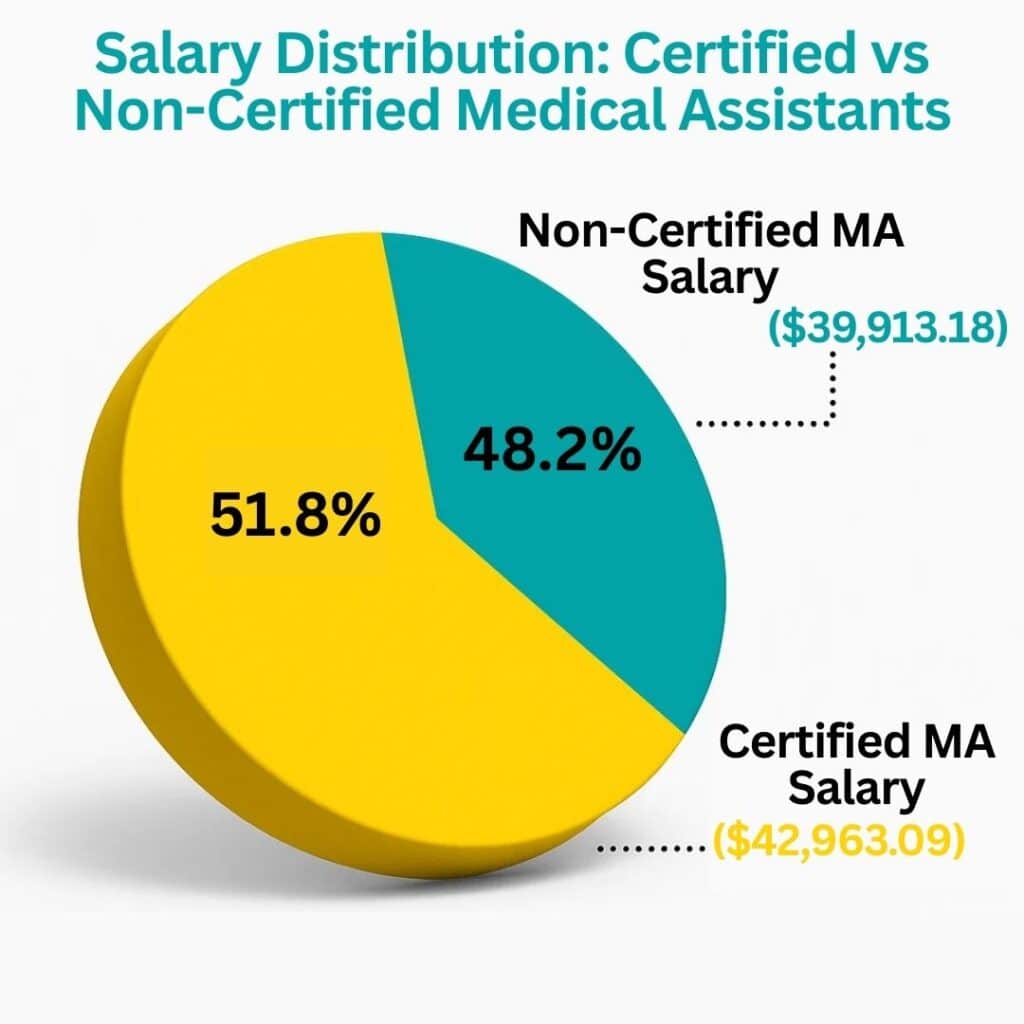
📊 Salary and Employment Insights
Pursuing certification not only enhances credibility but also directly impacts earning potential and job opportunities. Certified professionals tend to earn more and enjoy greater job security.
The graph below illustrates the salary comparison between certified and non-certified medical assistants, as well as the number of certified professionals and projected employment growth:
Source: aama
Education and Training
Both clinical medical assistants and healthcare support professionals typically complete post-secondary education programs designed for healthcare roles. These programs often include courses in anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, medical terminology, and hands-on training in clinical procedures.
While most states do not have specific education requirements for healthcare support professionals, some employers prefer candidates with an associate’s degree or certification from an accredited program. On the other hand, clinical medical assistants are required to have a high school diploma or equivalent and complete a post-secondary program specifically focused on clinical healthcare support.
What we provide
Virtual Medical Administrative Assistant
Medical Virtual Receptionist
Remote Medical Scribe
Medical Billing Virtual Asssistant
Executive VA & Virtual Office Manager
Virtual Dental Administrative Assistant
Dental Virtual Receptionist
Remote Dental Scribe
Dental Billing Virtual Assistant
Virtual Dental Executive Assistant
Patient Care Coordinator
Prior-Authorization
Provider Support
Telehealth Specialist
Telephone Triage
Remote Patient Monitoring
What Are Medical Assistants?
Medical assistants are multi-skilled medical professionals who support healthcare settings by performing both administrative tasks and clinical duties. Their role is essential for ensuring medical offices and clinics run efficiently.
Common Job Responsibilities of a Medical Assistant
A medical assistant’s job typically includes a mix of administrative duties and clinical skills:
Administrative Duties:
Scheduling appointments and reminding patients of their visits.
Maintaining medical records to ensure patient histories are accurate and up-to-date.
Answering phone calls and managing patient medical charts.
Handling clerical duties, such as greeting patients and collecting essential patient information during check-ins.
Checking patients in and collecting essential patient information during check-ins.
Clinical Responsibilities:
Recording vital signs like blood pressure, heart rate, and temperature.
Assisting with patient examinations by preparing patients and setting up necessary medical equipment.
Performing basic laboratory tests and analyzing lab tests.
Collecting medical histories to guide the healthcare team during patient support.
Medical assistants work in a variety of environments, including outpatient clinics, private practices, and hospitals. With their blend of administrative skills and clinical skills, they provide integral support to physicians and other medical professionals.
What Sets Clinical Medical Assistants Apart?
While all clinical medical assistants are healthcare support professionals, not all healthcare support professionals are clinical medical assistants. Confused? Don’t worry. Simply put, clinical medical assistants have a more hands-on role when it comes to direct interaction with patients and essential clinical tasks.
Clinical Medical Assistant Duties
The duties of clinical medical assistants include more clinical responsibilities and direct interaction with patients compared to general medical assistants. Their tasks often require advanced training, making them a valuable asset to any medical practice. Duties can include:
Preparing patients for procedures by explaining medical terminology and protocols.
Assisting doctors during patient examinations, surgeries, or minor procedures.
Conducting lab tests such as drawing blood and processing samples for analysis.
Administering medications or vaccinations under a physician’s supervision.
Taking detailed medical histories and helping physicians better understand patient needs.
Specialized Skills of Clinical Medical Assistants
Clinical medical assistants require advanced clinical skills alongside foundational knowledge and experience working directly with patients. They may also need proficiency in using medical equipment for diagnostic purposes, such as EKG machines. This hands-on expertise often positions clinical medical assistants as key players in ensuring a patient’s medical treatment is both thorough and timely.
Education Requirements for Medical Assistants and Clinical Medical Assistants
Becoming a Medical Assistant
Most healthcare support professionals, including medical assistants, start their careers with a high school diploma, but many employers prefer candidates who have completed a formal medical assisting program. These programs typically teach a combination of administrative skills, basic clinical skills, and familiarity with medical records and patient histories.
Some employers may also require certification, such as becoming a Certified Medical Assistant (CMA) or a Registered Medical Assistant (RMA).
Becoming a Clinical Medical Assistant
To pursue a role as a healthcare support professional specializing in clinical care, additional training focused on hands-on tasks is often required. Specialized continuing education courses may include topics such as reading and following medical charts and performing diagnostic lab tests.
Like their counterparts in general roles, some medical assistants choose to pursue certification to strengthen their credentials. Earning a CMA or RMA designation showcases your expertise in clinical tasks and medical support as a qualified healthcare professional.
Medical Assistant Program Accreditation
Medical assistant programs are accredited by either the Accrediting Bureau of Health Education Schools (ABHES) or the American Association of Medical Assistants (AAMA). These accrediting agencies ensure that medical assistant programs meet the necessary standards for education and training.
Accreditation is essential for medical assistant programs, as it provides students with the knowledge and skills required to become officially recognized healthcare support professionals. Many medical assistants choose to pursue certification, such as the CMA or RMA designation, which demonstrates their expertise and commitment to the field.
Workplace Settings for Medical Assistants vs Clinical Medical Assistants
General Medical Assistants
Medical assistants are commonly hired in settings that require a mix of administrative and clinical tasks. These include:
Family practices or primary care offices.
Outpatient clinics and surgery centers.
Specialty clinics, such as pediatrics or orthopedics.
Clinical Medical Assistants

Hospitals and surgical centers, where monitoring blood pressure is a routine part of patient care.
Hospitals and surgical centers, where medical assistants may help monitor vital signs such as blood pressure.
Specialized practices like cardiology or dermatology, where medical assistants may assist with monitoring blood pressure and other important health indicators.
The work environment may influence the specific tasks performed, but in any setting, clinical medical assistants serve as vital links between physicians, other medical professionals, and patients.
Certified Medical Assistant (CMA) and Registered Medical Assistant (RMA): Should You Get Certified?
While certification isn’t always required, having one can significantly boost your career prospects. Those who hold recognized credentials often gain access to better job opportunities, enjoy higher earning potential, and benefit from greater job security.
Clinical Medical Assistant vs Medical Assistant Jobs and Salaries
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the demand for medical assistants is expected to grow by 18% through 2030, much faster than the average for most professions. This is largely due to the increasing need for healthcare services.
Medical Assistant Salaries:
Medical assistant salaries vary depending on experience and location, but the average annual salary in the United States is approximately $37,000.
Clinical Medical Assistant Salaries:
Clinical medical assistants with specialized training may earn slightly higher salaries, with averages closer to $40,000 annually. Additional certifications may further raise earning potential.
Why Do Healthcare Facilities Hire Medical Assistants and Clinical Medical Assistants?
Healthcare providers bring medical assistants on board to ensure the efficiency of their medical office while delivering exceptional support to patients. Healthcare support professionals with a clinical focus play a more targeted role, concentrating on advanced tasks that support diagnostics and treatment. Employing both ensures a balanced operation where clerical responsibilities don’t compromise medical care.
Administrative tasks
Medical assistants are trained to handle a variety of office-related tasks, allowing healthcare facilities to run smoothly. These tasks may include managing patient records and billing and coding. By bringing medical assistants onto their team, healthcare providers can focus on providing quality services to their patients without the added stress of managing duties unrelated to direct interaction with patients.
Patient care
Medical assistants also play a crucial role in delivering hands-on support to patients. They may assist with preparing patients for examinations and collecting medical histories. This allows healthcare providers to spend more time with patients, improving the overall patient experience. Additionally, having these professionals on staff ensures that patients receive prompt attention and care when they need it.
Lab Tests and Procedures
Clinical medical assistants are responsible for performing basic laboratory tests and procedures, such as drawing blood and preparing samples for lab tests. They must have the necessary clinical skills and knowledge to perform these tasks safely and effectively.
Medical assistants may also assist with administering medications, measuring key health indicators, and preparing patients for medical procedures. In outpatient clinics, medical assistants may be responsible for handling additional duties, such as conducting patient interviews and taking medical histories.
Patient Education and Care
Medical assistants play a crucial role in patient education and care, providing patients with essential information about their medical conditions and treatment options. They must also be familiar with patients’ medical histories to communicate effectively, answer questions, and address concerns.
Medical assistants may also be responsible for providing health education to patients, teaching them about healthy habits and disease prevention. By offering outstanding support and education to patients, medical assistants can help improve patient outcomes and enhance the overall quality of care.
Job Outlook and Growth Prospects

By pursuing a career as a medical assistant, individuals can enjoy a rewarding and challenging profession with opportunities for advancement and professional growth. Credentialed healthcare support professionals, such as those with the CMA or RMA designation, may have an advantage in the job market, as they have demonstrated their expertise and commitment to the field.
Choosing Between Clinical Medical Assistant and Medical Assistant Careers
When comparing clinical medical assistant vs medical assistant roles, consider your interests and long-term career goals. If you’re drawn to tasks like greeting patients and maintaining medical charts, a career as a medical assistant might satisfy your aspirations.
On the other hand, if you’re passionate about tasks like drawing blood, assisting with evaluating patients, and performing lab tests, pursuing a career as a clinical medical assistant may be the better avenue.
Making the Leap into Medical Assisting
Whether you see yourself as a general medical assistant or a clinical medical assistant, the field offers rewarding opportunities for growth and meaningful contributions to supporting patients. With training programs widely available and certification options such as credentialed healthcare support roles like CMA and RMA, taking the first step toward a career in this profession is both achievable and worthwhile.
If you’re eager to join a healthcare team, start by exploring educational programs or certifications near you. Medical assistants play key roles in both administrative and clinical assistance, offering endless possibilities for a fulfilling career.


 Administrative Duties:
Administrative Duties: